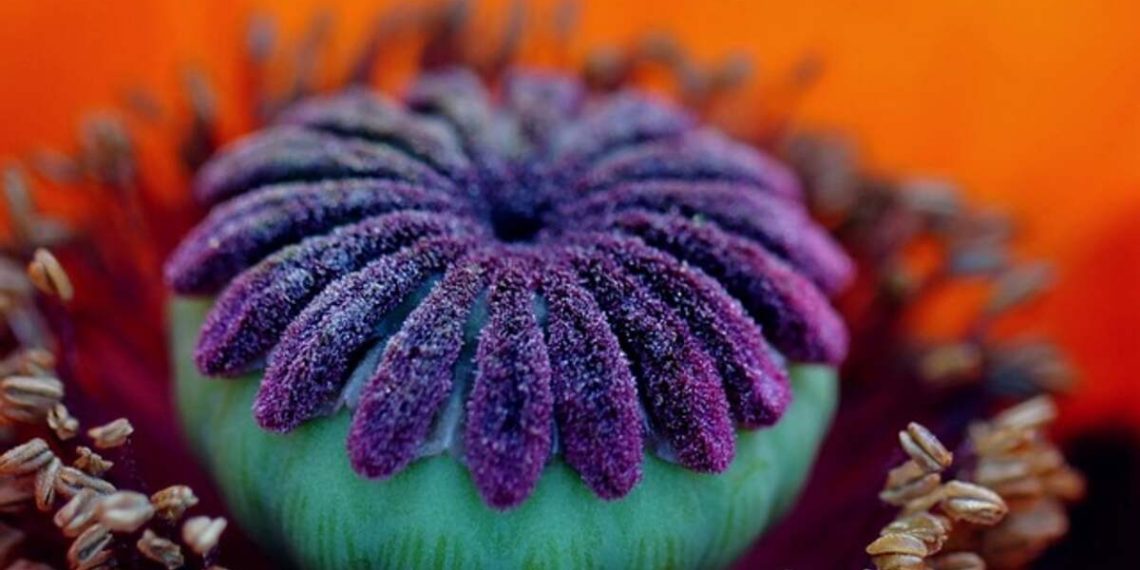
Papaver somniferum is widely cultivated around the world for its seeds and opium. These seeds can be used in food products, while opium is produced from its milky fluid that seeps out of incised pods. Check out the Best info about Dried poppy pods.
People commonly use the pods of poppies to prepare poppy seed tea, which has various therapeutic and psychoactive effects, including narcotic, analgesic, antidiarrheal, and psychoactive qualities. Long-term usage may lead to physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms when abruptly stopped.
Harvesting
Poppy seed plants produce bluish-green pods that open after their petals have withered, each containing thousands of tiny seeds. Harvesting occurs once weather conditions dry; otherwise, they rot in storage until harvest time. Unharvested pods open and release their seeds several feet from their respective plants, where new crops will eventually sprout the following season. Milky fluid seeping from cuts within unripe seed pods has long been used as an ingredient for making tea, which contains high concentrations of alkaloids such as morphine and codeine alkaloids which morphine and codeine alkaloids; seeping out cuts has long been used as an ingredient by civilizations alike!
The United States Drug Enforcement Administration has prohibited the cultivation of opium poppies (Papaver somniferum) to provide the raw material for making opium or heroin; it remains legal, however, to import poppy seeds and opium straw (i.e., stalks of Papaver somniferum without seed pod) from regulated countries for commercial purposes.
To produce opium, the seed pods of the poppy plant must first be crushed to release their juices and dissolved into the water to produce semi-solid material called “opium tar,” which can then be smoked directly or combined with other substances to create more potency drugs such as hashish and heroin.
Poppy pods can also be dried and utilized as ingredients in poppy seed tea (PST), which contains opioid alkaloids such as morphine, codeine, and thebaine that may lead to addiction and overdose, potentially leading to death. Consuming PST may lead to addiction or lead to a fatal overdose.
Poppy seeds should be planted either late fall or early spring for optimal germination and growth conditions. After planting, keep the soil moist until seedlings emerge; watering needs should decrease to approximately an inch per week until seedlings have matured further. Once established, watering should become less frequent before side-dressing plants with 21-0-0 liquid fertilizer as part of soil preparation or after thinning to stimulate robust growth. Once pods become ready to harvest in summer, walking along each row, inverting each pod, and shaking their seeds into a bucket or bag ensures optimal seed germination and maturity conditions!
Drying
Due to their easy care needs, poppies are an annual flower frequently grown for decorative dried bouquets and poppy seed head bunches. Keep the soil moist until seedlings have germinated and established themselves before only watering when necessary to ensure healthy development. Sun exposure and well-drained soil are essential for poppy seed heads. Compost or well-rotted manure in planting areas promotes healthy plant development while producing larger pods from your poppy plants.
Papaver somniferum, commonly referred to as the opium poppy or opium poppy, produces seed pods filled with milky sap that contains alkaloids such as morphine. While production may be legal in certain areas and requires a license in others, harvesting milky juice from its capsule is done using special tools that cut vertically with parallel strokes for easier harvesting of its milky sap, then scraped away using homemade tools before rolling up into small balls or lumps for sale.
Poppy seed harvest can occur either when an opium crop is grown or after it has matured and dried out. When intended for human consumption, they should usually be washed to remove most morphine alkaloids; however, trace amounts may still cause positive test results when tested using a urine opiate screen.
As seed pods dry, their leathery exterior cracks, with contents rattling inside. Depending on weather conditions, how quickly their contents dry will depend upon how you spread out to dry them; typically, this takes several weeks in an open, airy space indoors or out. Alternatively, their seed heads may be steamed or roasted to soften and facilitate their removal of seeds.
Opium poppy decorative flowers feature their distinct appearance but can be combined with other natural products to produce more artistic designs. For instance, they can be mixed with Avena Sativa oatmeal and Statice Tatarica leaves for additional texture and visual interest. Furthermore, these gorgeous blooms make beautiful centerpieces when suspended on branches as part of a dried floral arrangement.
Storing
Poppy seed pods have a longstanding tradition of use both as food and medicine. Poppy seeds have long been considered effective at treating mild aches and pains, acting as a painkiller, relaxing/sedating agent to treat insomnia or catarrh, loosening coughs and easing breathing, relieving breathing difficulties as an expectorant, and providing digestive relief. Their seeds can also be made into cosmetic products, including lipstick and lip balm, eaten whole, ground into powder form, or pressed for oil extraction.
Poppy seeds are an attractive, tasty addition to baked goods such as cakes, cookies, muffins, and breads, providing a nutty-sweet flavor with crunch. Furthermore, poppy seeds make a nutritious addition to salad dressings and bagel toppings as they provide calcium and iron.
Opium poppy (Papaver somniferum) seed pods have long been used to produce the drug opium and its semi-synthetic derivatives such as morphine, codeine, and heroin. When taken as prescribed by a doctor, these drugs provide potent analgesia that alleviates pain, suppresses coughs, and relieves diarrhea; when misused, they can create psychological and physical addictions with symptoms including abnormal mood swings, depression, paranoia, difficulty sleeping, etc.
Illegal poppy production occurs all around the world and is highly profitable to cultivate; drugs can be stored without losing potency over extended periods, making them perfect trade products that can be transported easily with minimal space required, making traffickers able to move large volumes of opium or heroin rapidly between countries.
In 1943, the United States started regulating poppy production. Though legal poppy farms exist in some places like Colorado and Montana, most opium comes from Afghanistan and Burma, where most are produced illegally. The government claimed their right to regulate cultivation was protected by treaty powers of Congress; the court agreed and upheld the Federal Opium Poppy Act as constitutional.
Preparation
Poppy seeds are an integral ingredient in many dishes, coming from the Papaver somniferum flowering plant and its latex that contains opioids such as morphine. Dried poppy seeds used for culinary use contain deficient alkaloids and should be considered safe to ingest. For optimal freshness when storing poppy seeds in the fridge, it is essential to properly prepare them before placing them in storage, as this will ensure their flavorful properties last over time without developing odors or unpleasant aromas.
To properly store poppy seeds in the fridge, transfer them from their original packaging into an airtight container. This will protect against moisture seeping in, which could otherwise spoil them. Furthermore, choosing an opaque storage vessel would be wise to avoid light damage during storage.
The Drug Enforcement Agency is cracking down on poppy seed cultivation. They have asked seedmen and flower shops to stop selling decorative poppy flowers and pods; companies are no longer allowed to include cultivation instructions on their packages, yet poppy seeds may still be purchased online and in certain stores.
Opium is produced by collecting the milky fluid that seeps from cuts in unripe poppy seed pods and scraping it off with a curved spatula before drying in open wooden boxes – eventually becoming medicinal products.
Legal cultivation of the opium poppy for medicinal use currently occurs in India and Turkey, where its value exceeds millions annually for its growers.
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has also aggressively pursued drug traffickers dealing in illegal heroin produced from poppy plants, issuing numerous cease and desist orders against traffickers caught selling poppy seeds. Many traffickers employ stamps to maintain brand recognition when caught by law enforcement officials – one infamous example is an Afghan heroin dealer using camel stamps to mark his products.
Read Also: The Rise of Bio Wine: A Look Into the Future of Viticulture